本文是我在上UCSD的 CSE 120: Principles of Operating Systems (Winter 2020) 整理的笔记,这一课主要介绍了操作系统里面死锁概念包括出现的原因,以及避免(防止出现)以及解决办法(出现死锁时最好的方法是重启大法!!)
Basic
Definition
- Set of processes are permanently blocked
- Unblocking of one relies on progress of another, but none can make progress
Example
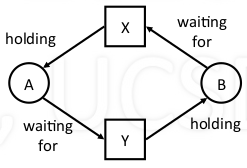
- Process A holding resource X, waiting for resource Y
- Process B holding Y, waiting for X
these two process will not be able to make any progress
Another example: memory
- Total memory = 200MB
- P1 holds 80MB, requests 60MB
- P2 holds 70MB, requests 80MB
- Set of processes are permanently blocked
Four conditions for Deadlock
- Mutual Exclusion
- Only one process may use a resouce at a time
- Hold-and-Wait
- Process holds resouce while waiting for another
- No Preemption
- Can’t take a resource away from a process
- Circular Wait
- The waiting process form a cycle
- Mutual Exclusion
Attack the Deadlock Problem
- Deadlock prevention
- Make deadlock impossible by removing one (or more)condition
- Deadlock Avoidance
- Avoid getting into situations that lead to deadlock
- Deadlock Detection
- Don’t try to stop deadlocks
- If they happen, detect and resolve
- Deadlock prevention
Attck the deadlock
Deadlock prevention
- Mutual exclusion -> relax where sharing is possible
- Hold-and-Wait -> Get all resources simultaneously (wait until all free)
- No preemption -> allow resources to be taken away
- Circular wait -> order all the resources, force ordered acquisition
Deadlock Avoidance
- Avoid getting into situations that lead to deadlock
- Selective prevention
- Remove condition only when deadlock is possible
- Works with incremental resource requests
- Resources are asked for in increments
- Do not grant request than can lead to a deadlock
- Need maximum resource requirements
Banker’s Algorithm
- Fixed number of processes and resources
- System state: either safe or unsafe
- Depends on allocation of resources to processes
- Safe: deadlock is absolutely avoidable
- Can avoid deadlock by certain order of execution
- Unsafe: deadlock is possible(but not certain)
- May not be able to avoid deadlock
Diagram
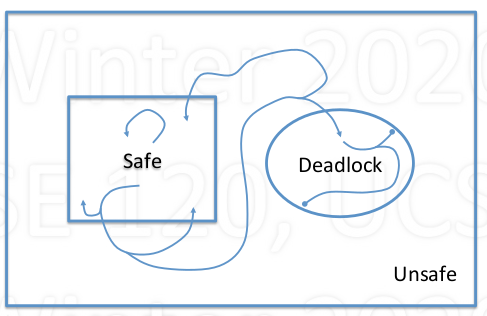
- Avoid getting into situations that lead to deadlock
Deadlock Detection (mostly used!)
Method
- Periodically try to detect if a deadlock occurred
- Do something (or nothing) about it
Resoning
- Deadlocks rarely happen
- Cost of prevention or avoidance not worth it
- Deal with them in special way (may costly)
Recovery from deadlock
- Terminate all deadlocked process (reboot)
- Terminate deadlocked processed one at a time
- need to detect