本文是我在上UCSD的 CSE 120: Principles of Operating Systems (Winter 2020) 整理的笔记,第一课主要介绍了操作系统以及进程的一些基本概念。
Definition
- Abstraction of a running program (dynamic)
- While program is just static code
Resources
- CPU
- Processing cycles (CPU time)
- Execute intstructions
- Memory
- Bytes or words
- maintain state
- Other resources (I/O)
- CPU
Context of a Process (machine and kernel-related state)
- CPU context
- PC (program counter)
- SP (stack pointer)
- FP (frame pointer)
- GP (general pointer)
- Memory context
- program code
- static variables(init, uninit)
- heap
- shared memory
- stack of activation records
- Other (kernel-related state, …)
- CPU context
Process memory structure
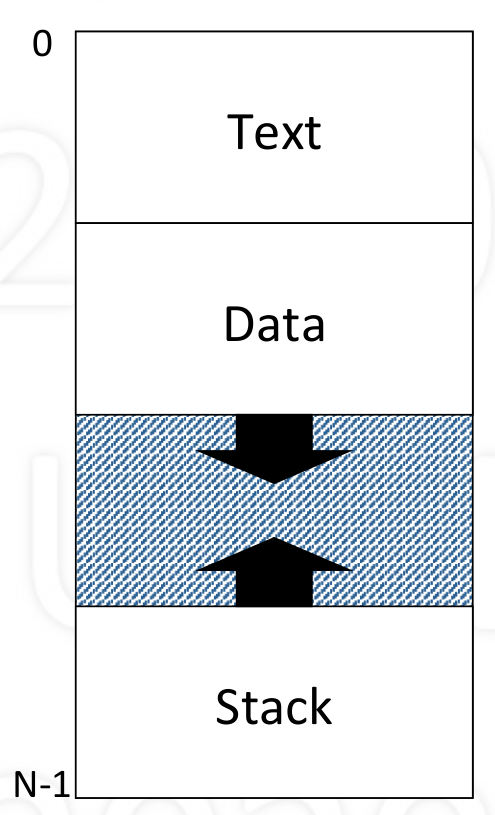
- Text area: code (program instruction)
- Data
- Global variable
- Static variable (local and global)
- Heap
- Stack
- Activation records
- Automatic growth/shrinkage
Process stack
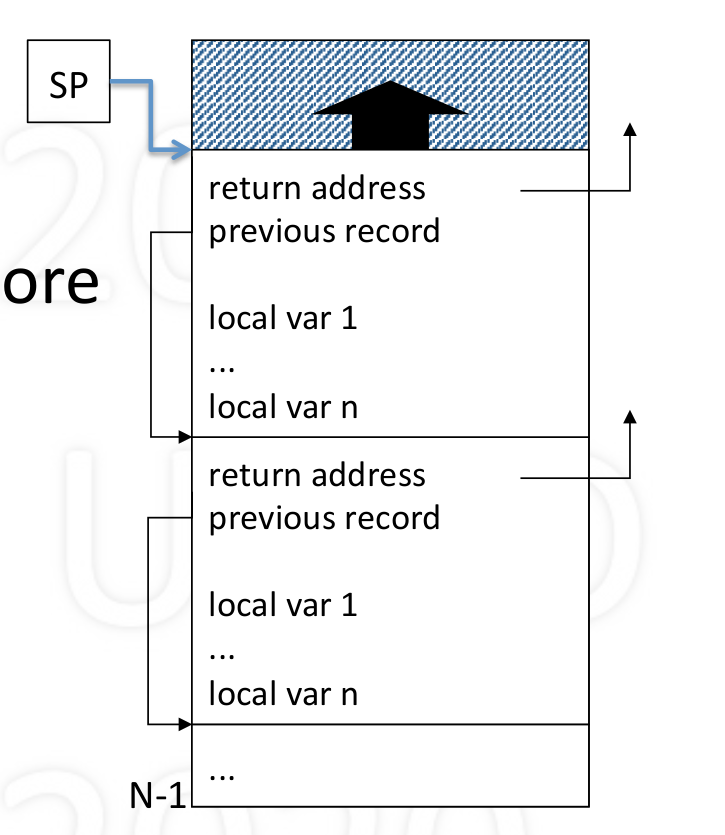
- Stack of activation records
- An activation records stores:
- return address
- link to previous record
- local varibale
- other
- Stack pointer points to top
Multi-Processes
- Goal: support several processes running “simultaneously” or let one process intentionally yield to another process
- Method: Context switching
- Switch process A (running) to process B (waiting) while store context (state) of process A (since it’s not finished)
- process
- save context of current process
- save GP
- save SP
- save PC
- load context of next process
- load GP
- load SP
- load PC (must be last, once PC is loaded, the process B begins to run (PC indicates instruction execution))
- save context of current process